Understanding food safety laws and the role of FSSAI in India
Defining FSSAI
FSSAI (food safety and standards authority of India) is an organization that governs, regulates and monitors the food business in India. Also, it is an autonomous body formulated under the ministry of health and family welfare, GoI. It is vital to conduct the process of food license registration in India.
FSSAI registration was set up under the Food Safety and Standards (FSS) Act, 2006, to keep an eye on the ever-increasing problem of food adulteration and mixing of additives since the food industry began to play a significant role in the economy. Also, the FSS act is an integrated statute that brought the provisions of various laws (prevention of food adulteration act, 1954, Milk and milk products, 1992, Vegetable and oil control order, 1947) and so forth under the one roof by laying down standards based-on scientific research and calculation for regulating the manufacturing, distribution, storage, sale and import by food businesses in India.
Reason for enactment
The FSS was brought into place to;
– Comprehensive laws in the country concerning food safety.
– Formulating a single point reference system.
– Also, for the establishment of FSSAI (food safety and standard authority of India).
– Employing safe food practices.
– For efficient monitoring, allotting licenses to food businesses.
– Ensuring compliance via penalties and inspections.
Present functions that FSSAI performs
– Making rules and regulations for laying down standards and guidelines of food safety.
– Also, allocating FSSAI food safety license and certificate for the food businesses.
– It also lays down the guidelines and procedures for laboratories in the food business.
– To offer recommendations to the government in framing new policies.
– It also collects data concerning contaminants in food products, locating the emerging risks and invoking the rapid alert system.
– To make an information network across the country about food safety.
– Promulgating general awareness about food safety and food standards.
The food processing industries are one of the largest industries in the country. It has the capability to contribute to the betterment of the agriculture economy, creating large manufacturing units and food chain outlets, which results in the creation of employment and export earnings.
General principles for food safety and articles of food
The FSS act has many regulations that the food business operators require to be followed, like food safety and standard (licensing and registration of food businesses) regulations, 2011. Also, food safety and standards (food product standards & food additives) regulations, 2011, food safety and standards (prohibition and restriction on sale) regulations, 2011, food safety and standards (contaminants, toxins and residues) regulations, 2011, food safety and standards (packaging and labelling) regulations, 2011 and so forth. These acts permit or proscribe the inclusion of substances in food that is consumable for humans.
The FSS Act proscribes the inclusion of harmful and unhealthy substances like insecticides in food. It also specifies that food articles should not contain any contaminant, natural toxic substances or toxins, heavy metals, hormones, pesticide residue, insecticide, antibiotic residue, veterinary drug residues so on and so forth.
It also states that if it is the unique, genetically modified article of food, organic food, irradiated food, foods for special dietary intakes, functional food, health supplements, nutraceuticals, and so forth. They are not allowed to be manufactured, distributed, sold, and imported into the country. Also, the act mentions special labelling for various kinds of foods and food business operators will have to obey the rules and requirements sternly. Imported food needs special requirements that have to be followed.
Packaging and labelling regulations.
As per the food safety and standards (packaging and labelling) regulations, 2011, FSSAI regulations are a complete set of guidelines that all food product brands and manufactures should abide with. It also inflicts 12 fundamental labelling regulations for any food packaging as given below;
– Food’s name.
– Ingredients list.
– Information related to nutrition.
– Vegetarian or non-vegetarian declaration of food.
– Food additives used declaration.
– Manufacturer’s name and address.
– Details for customer care.
– Quantity.
– Retail price rate.
– FSSAI license number and logo.
– Batch identification number, country of origin, marketing date.
– Instructions for usage.
FSSAI chooses the content architecture and the placement – what goes on front or back. The size of various texts, typefaces to be used, and the amount of area the information must cover all the food and beverage labelling.
FSSAI registration and license
Under the food safety and standards (licensing and registration of food businesses) regulations, 2011, FBO (food business operator) is needed to get a food license upon breaching the threshold limit of turnover. Also, the type of food license to be acquired relies on the business scale and the type of business activity that FBO is involved in. After the submission of required documents for the FSSAI license, the government authority will consider the application. There are 3 types of FSSAI licenses as given below;
- Basic FSSAI registration – it is compulsory for small FBOs. It is for those businesses whose turnover does not go beyond Rs. 12 lacs/annum. Also, it involves small retailers, hawkers, itinerant vendors, or temporary stallholders.
- State FSSAI license – is compulsory for the food businesses with annual turnover betwixt Rs. 12 to 20 crores. The turnover limit is the same for an FSSAI state manufacturing license or FSSAI state trading license.
- Central FSSAI license – it is compulsory for food businesses whose annual turnover is more than Rs. 20 crores in case of manufacturing or trading or storage beyond certain limits as mentioned by the laws.
Process of acquiring FSSAI registration
– It can be initiated by submitting form A to the food and safety department.
– Application can be accepted or rejected by the department within a week from the application date receipt, and rejection should be intimated to the applicant in writing.
– If accepted, then a registration certificate will be granted with the registration number and applicant’s photo.
– FBO should display the registration certificate at the place of business during business hours.
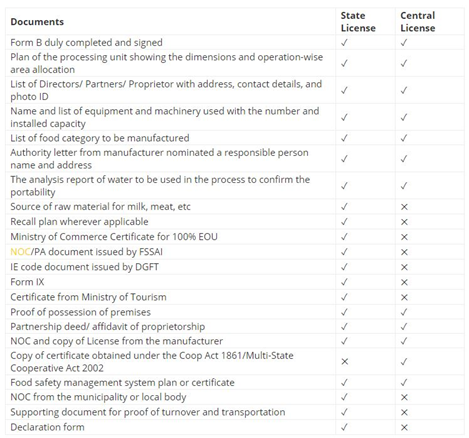
Required documents for acquiring an FSSAI license.=
Benefits of FSSAI food license
A food license can offer legal benefits, build goodwill, create customer awareness, expand business expansion, and ensure food safety. It also helps in regulating, manufacturing, storage, distribution and sale of import food.
Repercussions of non-compliances.
Food safety officers carry out inspections of FBO’s facility and identify their compliance level with the regulation using a checklist. Based on that, they give mark as following;
– Compliance (C).
– Non-compliance (NC).
– Partial compliance (PC).
– Not applicable/Not observed (NA).
Based-on the marks, officers might issue an improvement notice wherever needed according to section 32 of the FSS act, 2006. If the business operator cannot comply with the improvement notice, then his/her license will be cancelled after the show-cause notice. Further, any operator can appeal to the state commissioner of food safety if not satisfied with it. Also, the decision thereon can be challenged by appealing to the food safety appellate tribunal or HC.
Penalty
If one violates the rules, then one will have to pay the penalty. The penalty will be in the form of a fee or monetary charge. Keeping business under supervision, withdrawal of license, and routine inspection will be the penalty in the situation of grave violation or multiple accounts of rule-breaking.

Labdhi Kochar
Labdhi, associated with LegalWiz.in since 2016, is a Company Secretary, Business Manager and Consultant for the company. She helps startups by giving them consultations and insights on their business development and growth. Labdhi is a BCom-LLB and has 4 years of Industry experience.
